How To Reduce Age Spots: Causes, Treatment, and Prevention
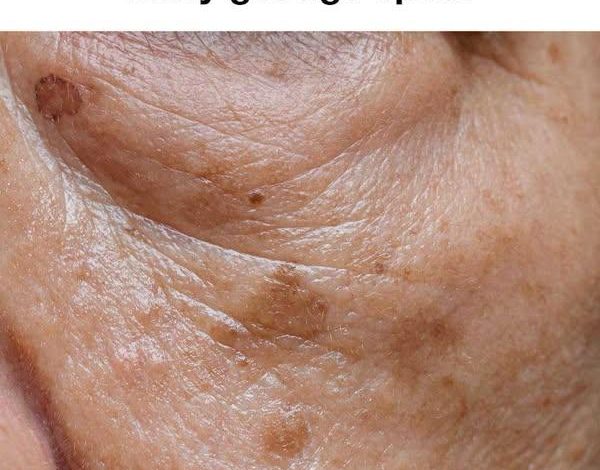
The journey of aging is a remarkable process, filled with experiences and growth. While we may sometimes focus on the physical changes that come with time, reaching an advanced age is a privilege many do not experience. Embracing this journey involves not fighting against aging itself, but rather focusing on maintaining our health and vitality as we mature. Our skin, being the body’s largest organ and most visible layer, plays a significant role in this. One common concern associated with aging skin is the appearance of what we commonly refer to as age spots. These spots can sometimes lead to feelings of self-consciousness. Fortunately, there are numerous effective strategies available for both preventing and treating these spots, allowing individuals to feel confident in their skin and maintain its health well into their later years.
What Exactly Are Age Spots?
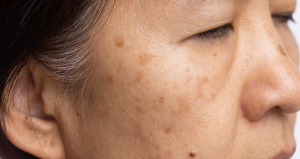
Age spots, also medically known as liver spots, sun spots, or solar lentigines, are essentially areas of darker pigmentation that develop on the skin as we get older. While they are most frequently observed in adults over the age of 50, they can also appear in younger individuals who have experienced significant sun exposure throughout their lives. It’s important to understand that age spots themselves are generally not a threat to your health and are often addressed for cosmetic reasons. However, the presence of numerous age spots can sometimes make it more challenging to identify new or changing spots that could potentially be a sign of skin cancer, such as melanoma. Encouragingly, the primary factor contributing to the development of age spots is also a major risk factor for skin cancer, meaning that the approaches to preventing both conditions are largely aligned.
Why the Name ‘Liver Spots’? A Historical Misunderstanding
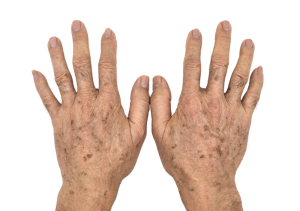
You might have heard age spots referred to as “liver spots.” This name originated from a historical, now outdated, belief that these skin blemishes were linked to problems with the liver. However, the term “liver spot” is indeed a misnomer. Modern medical understanding has clearly established that age spots have absolutely no connection to liver function or liver disease. The historical association likely stemmed from a lack of understanding regarding the true cause of these pigmented marks. We now know definitively that age spots are primarily the result of years of cumulative exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which leads to a localized overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Consequently, the terms “age spot” or “sun spot” are more accurate and are the preferred terminology used in dermatology to describe these pigmented skin lesions.
The Underlying Causes of Age Spots

The development of these hyperpigmented spots is a direct response to prolonged and significant exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, primarily from sunshine. Essentially, the pigment-producing cells in your skin, known as melanocytes, become overactive when exposed to UV radiation. This overactivity leads to an increased production of melanin in localized areas, causing the skin to darken as a protective mechanism against excessive sun exposure. Age spots are more prevalent in individuals with lighter skin tones, as their skin has less natural melanin to begin with. These spots most commonly appear on areas of the body that receive the most sun exposure over time, such as the shoulders, neck, face, hands, and sometimes the arms and legs.
Another contributing factor to the formation of age spots is a phenomenon called melanin clumping, where high concentrations of melanin accumulate in specific areas of the skin. Again, this is frequently triggered by exposure to the sun. However, sunlight is not the only source of UV radiation that can lead to age spots. The use of artificial tanning sources, such as tanning lamps and tanning beds, which also emit UV light, can similarly cause these sun-induced spots to appear. Your personal history of sun exposure, including the frequency and severity of sunburns you’ve experienced, can significantly influence the number, size, and color of age spots you may develop. As previously mentioned, it’s crucial to remember that the very same UV radiation that causes age spots is also a primary cause of melanoma, a serious form of skin cancer. Therefore, taking steps to prevent age spots is not just about maintaining a youthful appearance but, more importantly, about protecting yourself from a potentially life-threatening disease.
Recognizing Age Spots: Symptoms and Diagnosis
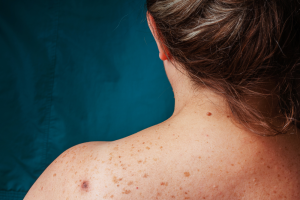
Age spots typically manifest as flat, oval-shaped patches of skin with increased pigmentation. Their color can vary from a light tan to a dark brown. They can also range in size, starting as small as freckles and growing to become much larger over time. In some cases, multiple age spots in close proximity can eventually merge together. Unlike freckles, which tend to fade during periods of reduced sun exposure, age spots do not disappear or lighten significantly with less UV exposure.
While sun spots are generally harmless from a health perspective, it is vital to be able to distinguish between benign liver spots and skin growths that could potentially be cancerous. Spots that exhibit a very dark or black coloration may warrant closer attention for potential malignancy. Similarly, any skin spot that undergoes changes in its appearance, whether in size, shape, color, or texture, should be viewed with caution. Spots with unusual or uneven coloring, ragged or poorly defined edges, or any that exhibit bleeding, should all be promptly evaluated by a qualified medical professional. It is a good practice to consult your doctor or a dermatologist whenever you notice any new or changing spots on your skin to ensure proper diagnosis and care.
Effective Treatments for Age Spots

As previously stated, age spots are not medically dangerous and do not necessitate treatment for health reasons. However, if you are concerned about their appearance, there are several effective methods available to improve their visibility. These treatments aim to either remove the age spots entirely or significantly lighten their pigmentation for cosmetic purposes. It is crucial to emphasize that all cosmetic treatments for age spots should be performed by a skilled and licensed dermatologist. Typically, the process will begin with an initial consultation where you can discuss your specific skin concerns and goals with the dermatologist. They will then help you develop a personalized treatment plan that is safe, effective, and aligned with your expectations. Common cosmetic treatments for age spots include:
Chemical Peels

Chemical peels are a widely used cosmetic procedure designed to enhance the appearance of age spots and other skin irregularities. During this procedure, a chemical solution is carefully applied to the skin, causing the outermost layers to exfoliate or peel off. This process reveals the underlying skin, which is often smoother and less pigmented. The strength of the chemical solution used in the peel can vary depending on the severity of the pigmentation. Superficial peels target mild discoloration, while deeper peels penetrate further to address more pronounced pigmentation issues like age spots. Chemical peels work by fading sun spots, reducing overall pigmentation, and improving the skin’s tone and texture. They achieve this by promoting the turnover of skin cells and stimulating the production of collagen, a vital protein for skin health. It is essential to reiterate that chemical peels should only be administered by a licensed dermatologist who can assess your skin type and ensure the procedure is performed safely and effectively.
Dermabrasion
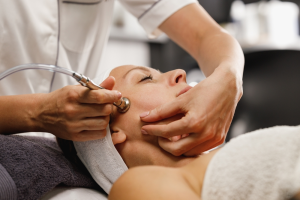
Dermabrasion is another cosmetic procedure employed to improve the appearance of age spots and other skin imperfections. In this technique, a dermatologist utilizes a high-speed rotary instrument equipped with an abrasive wheel or brush to gently remove the superficial layers of the skin. Essentially, this process involves carefully “sanding” down the areas of pigmented skin. By removing these outer layers, dermabrasion encourages the growth of new skin cells, resulting in smoother skin with a more even tone and texture. By specifically targeting the layers of skin where age spots are located, dermabrasion can effectively diminish their appearance and improve overall skin discoloration. It is important to recognize that dermabrasion is considered an invasive procedure that requires careful consideration and a thorough consultation with a qualified dermatologist. They can assess your individual skin type and condition to determine if dermabrasion is a suitable treatment option and discuss any potential risks involved. Following the procedure, meticulous aftercare and consistent sun protection are crucial for achieving the best possible results in treating age spots with dermabrasion. It is advisable to choose a dermatologist with whom you feel comfortable and well-cared for, and who has a proven track record of successful dermabrasion procedures.
Laser Resurfacing
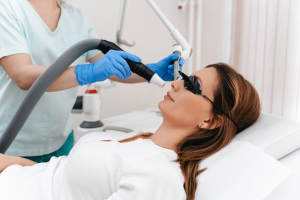
Laser resurfacing has become a popular cosmetic procedure for targeting age spots and uneven skin tone. During this treatment, a dermatologist uses focused beams of laser light to precisely remove the outer layers of skin that contain age spots, as well as scars and other imperfections. This controlled removal of the outer layers stimulates the production of collagen and encourages the growth of new, healthy skin cells, ultimately leading to a smoother and more evenly toned skin surface. The targeted laser energy works by breaking down the excess melanin that is responsible for the formation of age spots, while simultaneously promoting the skin’s natural healing process. This results in a noticeable reduction in pigmentation and an overall improvement in the skin’s appearance. Laser resurfacing treatments can be highly customized to address specific areas of concern and varying degrees of pigmentation, making it a versatile and personalized option. However, it is essential to consult with a dermatologist to determine the most appropriate type of laser treatment for your individual skin needs and to receive detailed instructions on proper post-treatment care to ensure optimal outcomes.
Skin Biopsy
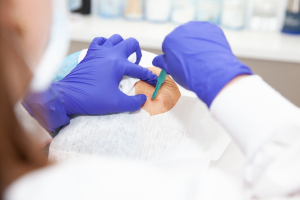
A skin biopsy is a medical procedure that involves the removal of a small sample of skin tissue for microscopic examination. While skin biopsies are primarily used to diagnose various skin conditions, they can also play a role in evaluating suspicious or changing age spots. During a skin biopsy, a dermatologist will first numb the area and then carefully remove a small piece of skin. This sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis by a pathologist. By examining the skin tissue under a microscope, pathologists can determine the precise nature of the age spot, whether it is benign or potentially harmful, and recommend appropriate treatment options if necessary. It is important to understand that a skin biopsy is not typically a treatment intended to remove or improve the appearance of all sun spots. Rather, it is a valuable diagnostic tool that can provide crucial information about the underlying causes of age spots, helping to guide further management and ensure proper care for individual skin concerns. If you have any age spots that are concerning, rapidly changing, or otherwise unusual, it is essential to consult with a dermatologist for a thorough evaluation to determine if a skin biopsy is necessary for accurate diagnosis and the development of an appropriate treatment plan.
Preventing Age Spots: A Proactive Approach

While the treatment options discussed above are readily available, they can sometimes be quite costly. A more economical and ultimately more beneficial approach for your overall skin health is to prevent age spots from forming in the first place. This primarily involves consistent and effective sun protection. While exposure to sunlight and UV radiation is indeed important for the body’s synthesis of vitamin D, the amount of exposure needed is actually quite minimal. The specific duration of exposure and the amount of skin that needs to be exposed will vary depending on several factors, including your geographical location, the time of year, the time of day, the current UV index, and your individual level of skin pigmentation. Individuals with very light skin tones will generally require shorter periods of sun exposure on their arms and legs to produce sufficient vitamin D, while those with darker skin tones may need three to six times more exposure to achieve the same result. If you have any uncertainties about your vitamin D levels or safe sun exposure practices, it is always best to consult with your dermatologist or primary care physician.
To minimize the risk of developing age spots, the most effective strategy is to limit your exposure to UV light. First and foremost, this means completely avoiding tanning beds and sun lamps. Secondly, it entails consciously avoiding intentional “tanning” in general. This means discontinuing the use of tanning oils and always using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of 30 or higher. It is generally recommended to avoid direct sun exposure during the peak UV radiation hours, which are typically between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m. When you are outdoors, consistently apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a minimum SPF of 30 to all exposed skin. Reapplication is crucial; it is generally recommended to reapply sunscreen every two hours, or immediately after swimming or excessive sweating, even if the product is water-resistant. In addition to sunscreen, physical protection in the form of appropriate clothing and hats that offer UV protection is considered the gold standard. In hot, sunny climates, opt for wide-brimmed hats that shade your face, neck, and ears, and wear loose-fitting, light-colored clothing – long sleeves and pants offer the best protection.
The Role of Zinc in Addressing Age Spots

Zinc is a vital mineral and micronutrient that plays a significant role in maintaining overall skin health. It is essential for promoting collagen synthesis, which is a key structural component of the skin, providing it with strength and elasticity. As we age, natural collagen production decreases, so supporting its synthesis can help keep your skin looking smoother and more youthful. By contributing to collagen production, zinc aids in the maintenance of healthy skin and the repair of damaged tissues, making it crucial for skin regeneration. Furthermore, zinc oxide, a common derivative of zinc, is widely used in sunscreens due to its effective UV-protective properties. There are two main types of sunscreens: chemical and physical. Zinc-based sunscreens act as a physical barrier on the skin’s surface, reflecting and scattering harmful UV radiation. This not only safeguards the skin from sun damage, which is a primary cause of age spots, but also avoids the use of chemical filters that may raise concerns for some individuals.
Zinc supplements and topical zinc-based creams and ointments may also play a role in the management of age spots. Zinc has been utilized in dermatology for the treatment of various skin conditions, including pigmentary disorders like melasma, suggesting its potential applicability in addressing age spots as well. A study published by the National Center for Biotechnology Information explored the therapeutic uses of both topical and oral zinc for a range of dermatological conditions, highlighting its versatility and potential in managing skin pigmentation issues. While the role of oral zinc supplementation in directly addressing age spots is less clearly understood and may primarily be beneficial in addressing underlying zinc deficiencies that could contribute to skin pigmentation problems, topical zinc formulations can directly target age spots. This is potentially due to zinc’s antioxidant and skin-regenerative properties. As with any supplement or topical treatment, it is always advisable to consult your doctor or dermatologist before starting any oral zinc supplementation or using over-the-counter topical zinc products to ensure they are appropriate for your individual needs and health status.
Exploring Natural Remedies for Age Spots

A quick search online will undoubtedly yield numerous websites and social media accounts promising remarkable results from the use of various “natural remedies” for age spots. These remedies, often including ingredients like lemon juice, apple cider vinegar, aloe vera, and green tea, have gained popularity for their purported ability to reduce the appearance of these spots. Lemon juice contains citric acid and vitamin C, both of which are believed to possess skin-lightening properties that may help to fade age spots over time. Similarly, apple cider vinegar is often promoted for its acidic nature, which some believe can exfoliate the skin and potentially lighten pigmentation. Aloe vera is well-known for its soothing and moisturizing properties, which may contribute to improved skin texture and a reduction in the visibility of age spots. Green tea, rich in antioxidants, has been studied for its potential to protect the skin from UV-induced damage and may also have skin-brightening effects, thus potentially offering benefits for age spots. While these natural ingredients can indeed offer various benefits for the skin, it’s important to have realistic expectations. For individuals with a significant number of dark sun spots and other pronounced pigmentation issues, these remedies are unlikely to replicate the results achievable through professional dermatological procedures.
Furthermore, it is crucial to remember that the term “natural” does not automatically equate to “safe” or “without potential side effects.” The same caution applies to all of these natural remedies for age spots. While they may offer certain benefits when used correctly, improper application or overuse can potentially lead to skin irritation or other adverse reactions. It is always a wise decision to consult with a healthcare professional, such as your doctor or dermatologist, before trying any new natural remedy for age spots. While generally considered safe for many people, natural ingredients can still cause allergic reactions or interact negatively with existing skin conditions or medications. Your dermatologist can help you determine whether these natural remedies are appropriate for your specific skin type, sensitivity, and overall health. They can also provide guidance on the proper application and dosage of these remedies to maximize potential benefits while minimizing any risks. In situations where age spots are persistent, rapidly changing, or causing you concern, seeking professional medical advice is strongly recommended to explore more effective treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
The Key Takeaway

Age spots are a common and natural part of the aging process, and there is absolutely no reason to feel ashamed of them. If you live long enough to develop age spots, it likely means you have spent time outdoors enjoying the sunshine, which is something to be appreciated. However, it is also perfectly understandable to want to prevent their formation or reduce the appearance of existing ones. The encouraging news is that the very same steps you should take to prevent and treat age spots are also crucial for preventing and detecting skin cancer. It is important to reject the notion that having a tan is somehow better or more desirable; your natural skin color is beautiful, whether you have a very light or very dark complexion. Regardless of your skin tone, protecting your skin from the damaging effects of UV radiation should be a priority for everyone. As always, before initiating any new treatment for sun spots, whether it involves natural remedies or more conventional methods, it is essential to consult with a qualified dermatologist. They can provide personalized guidance and help you determine the treatment options that are most suitable and safe for your individual needs and skin type.




